STARS program call for applications available at the ‘Functional Nanomaterials’ group, Department of Organic Chemistry, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic.
[Link]
All posts by MJB
Carbon nitride vs. graphene – now in 2D!
Cooper, A. I.; Bojdys,* M. J. Materials Today 2014, 17, 468–469.
A polymer laboratory might not be your first port-of-call for replacement materials for silicon in sensors and transistors, but polymer chemistry and organic synthesis may have much to offer here: enter the world of modular chemical design of new 2-dimensional materials.
DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod.2014.10.001 [Download]
This article is published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-No Derivatives License (CC BY NC ND) in final form at [DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod.2014.10.001].
“gt-C3N4—The First Stable Binary Carbon(IV) Nitride” – by Prof. Dr. Edwin Kroke
“Twenty-five years ago a diamondlike C3N4 phase was postulated. After many unsuccessful attempts the synthesis of an s-triazine-based modification was accomplished, which is reported to show interesting semiconducting and catalytic properties similar to that of graphene and related graphitic C/N/H phases.” – Prof. Dr. Edwin Kroke
Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014. [DOI: 10.1002/anie.201406427]
Highlight for the article: Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S. Y.; Björkman, T.; Palgrave, R. G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Rabe, J. P.; Kaiser, U.; Cooper,* A. I.; Thomas, A.; Bojdys,* M. J. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53, 7450–7455, [DOI: 10.1002/anie.201402191]
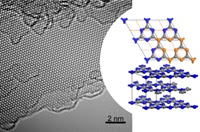
Frontispiece: Triazine-Based Graphitic Carbon Nitride: a Two-Dimensional Semiconductor
Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S. Y.; Björkman, T.; Palgrave, R. G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Rabe, J. P.; Kaiser, U.; Cooper,* A. I.; Thomas, A.; Bojdys,* M. J. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53, 7450–7455.
Graphitic Carbon Nitride
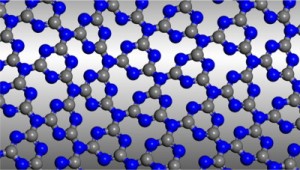
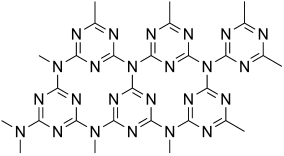
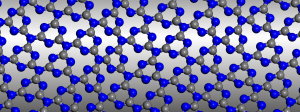
In their Communication on page 7450 ff., A. I. Cooper, M. J. Bojdys, et al. report crystalline thin films of triazine-based graphitic carbon nitride (TGCN). TGCN is structurally similar to graphite but it is a semiconductor, and the thin films display a direct bandgap between 1.6 and 2.0 eV.
Openings in the ‘Functional Nanomaterials’ group
Call for applications available at the ‘Functional Nanomaterials’ group, Department of Organic Chemistry, Charles University in Prague, Czech Republic starting at the earliest from August 2014.
“Designer 2D material may take us beyond graphene’s limits” – by Chris Lee
“A decade of work reveals chemically inert 2D semiconductor with decent bandgap.”
[Link] to full article
Chris Lee / Chris writes for Ars Technica’s science section. A physicist by day and science writer by night, he specializes in quantum physics and optics. He lives and works in Eindhoven, the Netherlands.
Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S. Y.; Björkman, T.; Palgrave, R. G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Rabe, J. P.; Kaiser, U.; Cooper,* A. I.; Thomas, A.; Bojdys,* M. J. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53, 7450–7455, [DOI: 10.1002/anie.201402191]
Press highlights for triazine-based graphitic carbon nitride (TGCN)
- Electronics Weekly – Improving transistors with graphene-type material by Alun Williams
- Before It’s News – Researchers fabricate graphene-like TGCN for the first time
- Graphene-info – Researchers fabricate graphene-like TGCN for the first time
- eWallstreeter – New graphene-type material created
- Nanowerk – Chemists create new graphene-type material
- Phys.Org – New graphene-type material created
- e! Science News – New graphene-type material created
- Nature World News – Researchers Create a Graphene-Like Material
- Engineering Specifier – New graphene-type material created
Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S. Y.; Björkman, T.; Palgrave, R. G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Rabe, J. P.; Kaiser, U.; Cooper,* A. I.; Thomas, A.; Bojdys,* M. J. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53, 7450–7455. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201402191
Triazine-Based, Graphitic Carbon Nitride: a Two-Dimensional Semiconductor
Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S. Y.; Björkman, T.; Palgrave, R. G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Rabe, J. P.; Kaiser, U.; Cooper,* A. I.; Thomas, A.; Bojdys,* M. J. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53, 7450–7455.
Graphitic carbon nitride has been predicted to be structurally analogous to carbon-only graphite, yet with an inherent bandgap. We have grown, for the first time, macroscopically large crystalline thin films of triazine-based, graphitic carbon nitride (TGCN) using an ionothermal, interfacial reaction starting with the abundant monomer dicyandiamide. The films consist of stacked, two-dimensional (2D) crystals between a few and several hundreds of atomic layers in thickness. Scanning force and transmission electron microscopy show long-range, in-plane order, while optical spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and density functional theory calculations corroborate a direct bandgap between 1.6 and 2.0 eV. Thus TGCN is of interest for electronic devices, such as field-effect transistors and light-emitting diodes.
This is the pre-peer reviewed version of the following article: Algara-Siller, G.; Severin, N.; Chong, S. Y.; Björkman, T.; Palgrave, R. G.; Laybourn, A.; Antonietti, M.; Khimyak, Y. Z.; Krasheninnikov, A. V.; Rabe, J. P.; Kaiser, U.; Cooper,* A. I.; Thomas, A.; Bojdys,* M. J. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53, 7450–7455, which has been published in final form at [DOI: 10.1002/anie.201402191].
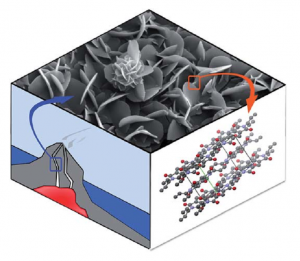
Geomimetics for Green Polymer Synthesis: Highly Ordered Polyimides via Hydrothermal Techniques
Baumgarten, B.; Bojdys, M. J.; Unterlass,* M. M. Polymer Chemistry 2014, 5, 3771-3776.
Inspired by geological ore formation processes, we apply one-step hydrothermal (HT) polymerization to the toughest existing high-performance polymer, poly(p-phenyl pyromellitimide) (PPPI). We obtain highly-ordered and fully imidized PPPIs as crystalline flakes and flowers on the micrometer scale. In contrast to classical 2-step procedures that require long reaction times and toxic solvents and catalysts, HT polymerization allows for full conversion in only 1 h at 200 °C, in nothing but hot water. Investigation of the crystal growth mechanism via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) suggests that PPPI aggregates form via a dissolution-polymerization-crystallization process, which is uniquely facilitated by the reaction conditions in the HT regime. A conventionally prefabricated polyimide did not recrystallize hydrothermally, indicating that the HT polymerization and crystallization occur simultaneously. The obtained material shows excellent crystallinity and remarkable thermal stability (600 °C under N2) that stems from a combination of a strong, covalent polymer backbone and interchain hydrogen-bonding.
Baumgarten, B.; Bojdys, M. J.; Unterlass,* M. M. Polymer Chemistry 2014, 5, 3771-3776 – Reproduced by permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry
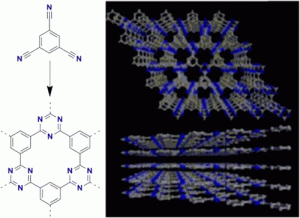
Covalent Triazine Frameworks Prepared from 1,3,5-Tricyanobenzene
Katekemol, P.; Roeser, J.; Bojdys, M. J.; Weber, J.; Thomas,* A. Chemistry of Materials 2013, 25, 1542–1548.
A novel covalent triazine framework (CTF-0) was prepared by trimerization of 1,3,5-tricyanobenzene in molten ZnCl2. The monomer/ZnCl2 ratio, the reaction time, and temperature significantly influence the structure and porosity of such networks. XRD measurements revealed that crystalline frameworks can be formed with surface areas around 500 m2 g-1 and high CO2 uptakes. Increasing the reaction temperature yielded an amorphous material with an enlarged surface area of 2000 m2 g-1. This material showed good catalytic activity for CO2 cycloaddition.
DOI: 10.1021/cm303751n [Download]
Reprinted with permission from Katekemol, P.; Roeser, J.; Bojdys, M. J.; Weber, J.; Thomas,* A. Chemistry of Materials 2013, 25, 1542–1548. Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society.